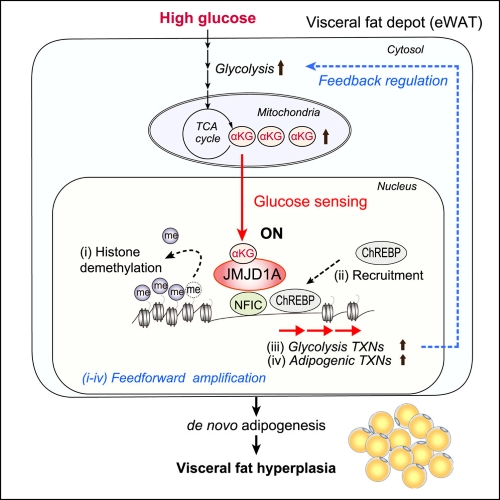
Glucose-activated JMJD1A drives visceral adipogenesis via
α-ketoglutarate-dependent chromatin remodeling.
Cell Reports (2025) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116060
We have elucidated the mechanism by which sugar rewrites the epigenome and forms new fat cells.
The results of this research are expected to contribute to elucidating the mechanisms of obesity
and diabetes.
This research was started by Dr. Eko and Dr. Matsumura at the Sakai lab of the RCAST of the
University of Tokyo. It was then published as a paper thanks to the efforts of many members,
including Assistant Prof. Arai, Assistant Prof. Ito, and graduate students Yang san and Debby
san in Tohoku University.
This is a collaborative research project with Prof. Sakai and Associate Prof. Yoneshiro of
Tohoku University, Prof. Soga of Keio University, Prof. Inagaki Of Gunma University, and Prof.
Osborne of Johns Hopkins University.
・Akita University Press Release (Japanese only)
・Tohoku University Press Release (Japanese
only)
・Nikkei Newspaper (Japanese
only)
・Akita Sakigake Shinpo (Japanese only)
Select Language
日本語 / English
